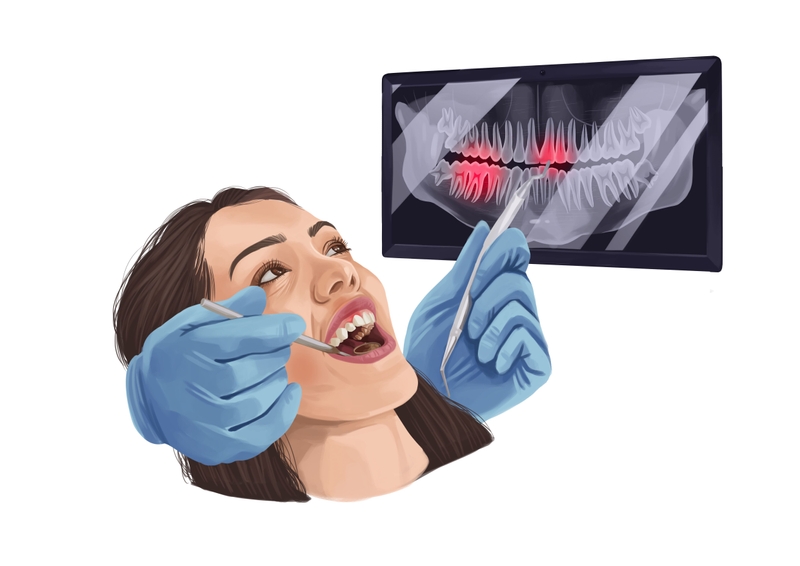
- Gum recession, or gingival recession, is a process in which the soft tissues pull back from the teeth. Gum recession exposes more of the dentition.
- Receding gums make the mouth more susceptible to diseases such as gum disease and can be painful. Genetics, oral hygiene, tobacco use, teeth grinding or clenching, aggressive brushing, and gum disease are all causes of this condition.
- Treatment of gum recession depends on the stage of progression. It may include a thorough cleaning, medication, or surgery.
Need urgent help with receding gums? Find a dentist open nearby with Authority Dental.
Receding gums occur when gum tissue pulls back from the teeth, exposing the roots. Learn the meaning, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Symptoms of receding gums
Picture by Authority Dental under CC 2.0 license
Gums are in your mouth to protect your roots, keep your teeth in place, and provide a barrier against bacteria. When they begin to recede, you may experience a plethora of dental issues. It is best to catch the problem early in order to prevent lasting damage.
The most common signs of receding gums include:
exposed tooth roots,
teeth looking longer than before, or being able to see the margins on crowns,
gums appearing “frayed” near the edges,
bleeding when you are brushing,
red or swollen gums,
changes to the bite,
pain, and
The first thing you can usually notice is sensitivity to hot and cold foods and drinks. This is because tooth roots become exposed. Instead of hard dentin, they are covered with cementum, which is a lot more vulnerable to stimuli.
Receding gums are also associated with pain when biting or chewing, or even when you are brushing your teeth. It is not uncommon to see redness in the toothpaste you spit out. It might become increasingly complex to combat bad breath as bacteria accumulate in the pockets between the gums and teeth.
Often, it is easy to notice that your gums have changed shape. This means the problem is already severe, and you should seek treatment.
What causes receding gums?
Receding gums are usually caused by a mixture of the following:
Periodontal disease
The leading cause of gum recession is periodontal disease. This is a bacterial infection of the gums and supporting structures in the jaws. Periodontal pockets can become very deep, and teeth may start to feel loose.
Genetics
Some people are more susceptible to gum recession and disease due to genetics. About 30% of the US population may have a predisposition to gum disease, regardless of how well they care for their mouths.
Aggressive brushing or poor oral hygiene
If you brush your teeth incorrectly, too hard, or with inappropriate products, you can easily damage your gums. If you feel tenderness after brushing, switch to a soft-bristled brush and a paste with little or no irritating ingredients. Whitening products are not recommended for those with sensitive gums.
Gums tend to begin receding on the left part of the mouth, around the outside of the arch. This is because most people are right-handed and put the most pressure on that area while brushing. If this is the case, it is time to think about learning to brush more gently. Using electric toothbrushes can also help, as their vibrating or rotating action is much gentler than hard back-and-forth brushing.
This does not mean you should neglect to clean your mouth. Those who do not brush and floss every day and miss out on bi-yearly dental cleanings are also at higher risk of gum recession.
Hormones
Women are particularly prone to gum issues due to hormonal changes. Puberty, pregnancy, and menopause are all periods in a woman’s life when gum recession is more likely.
Tobacco
Any products containing tobacco and nicotine are hard on the soft tissues in your mouth. Plaque is also more likely to stick to your teeth if you chew tobacco.
Grinding and orthodontic issues
Clenching and grinding your teeth, crooked dentition, and misaligned bites all work towards putting extra pressure on your gums. If you believe orthodontic issues are a problem, report to a specialist. The more teeth shift, the more tissue you may lose.
Age
A big risk factor for gum loss is age. Many people over 60 have some stage of gum recession around at least one tooth.
Certain diseases
Several medical conditions, such as diabetes and HIV, also increase the risk of developing gum recession. Drugs like antidepressants can also lead to dry mouth.
Foreign objects
Ill-fitting dentures can irritate the gums and cause gum recession. The same goes for any foreign objects in the mouth, like lip and tongue piercings. However, when it comes to piercings, there is no difference if they fit well. Their presence can cause gum recession.
In addition to proper brushing, flossing, and regular dental visits, some individuals explore ways to support overall gum health as part of their daily routine. Oral probiotics are designed to support a balanced oral microbiome, which may play a role in maintaining healthier gums when used alongside good oral hygiene practices. These supplements are not intended to treat or reverse gum recession and should never replace professional dental care. Anyone experiencing receding gums should consult a licensed dental professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.

How to fix receding gums?
Treatment for receding gums depends on the stage of progression. It can be diagnosed during dental exams. The dentist uses a probe to measure your gum pockets. The National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research states that these should range between 1 and 3 mm. Any larger pocket size indicates a problem.
A dental nurse or hygienist can also perform this before a prophy. The process of receding gums takes a long time, but it is still best to catch it early on. Do not neglect regular visits to the dental office. Your dentist may also refer you to a periodontist.
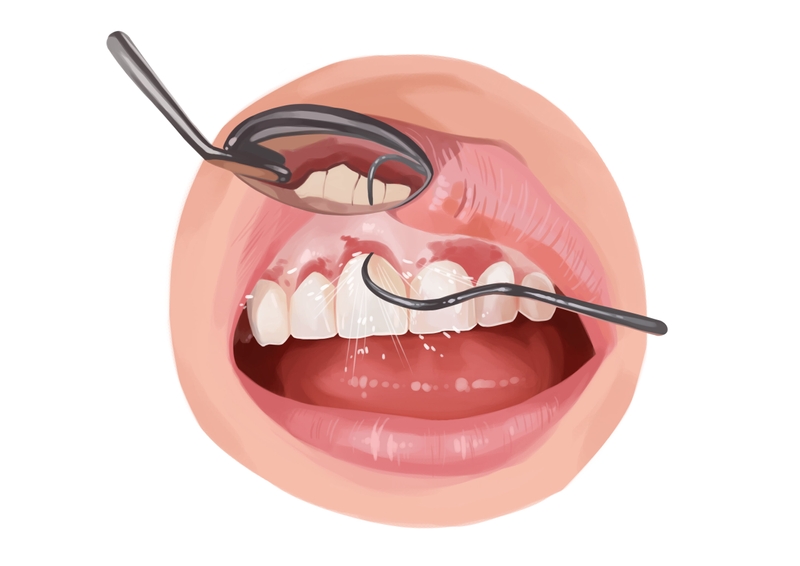
Scaling and root planing
Picture by Authority Dental under CC 2.0 license
The first step in receding gums treatment is often a deep cleaning. Plaque and tartar buildup are removed from the surface of the teeth with the help of an ultrasonic device. The dentist then cleans exposed root surfaces to allow the gums to shrink back and reattach.
If the problem is severe, especially if the gums have receded significantly, this might not be enough.
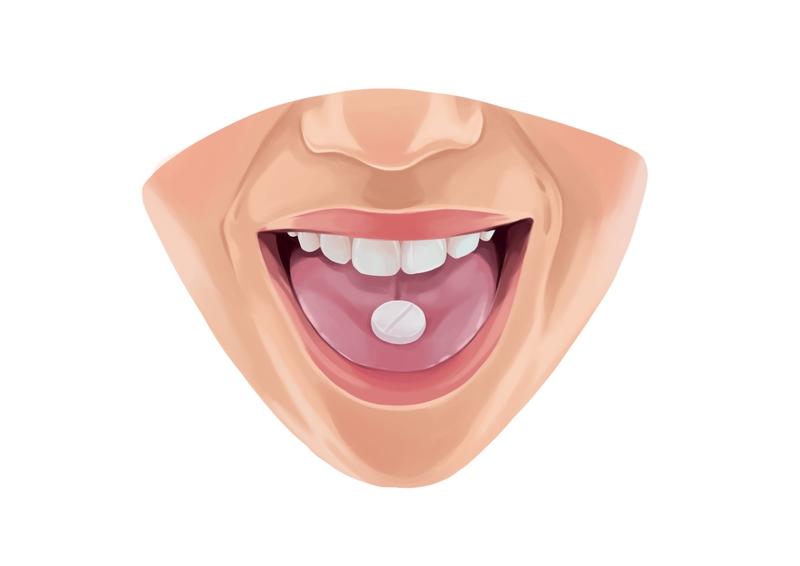
Medication
Picture by Authority Dental under CC 2.0 license
Prescribed medication can help to fix receding gums. This usually takes the form of time-release antibiotics placed or injected directly into your soft tissues. If the problem is not severe, other options include:
topical antibiotic gel,
antiseptic chips,
antimicrobial mouthwash, or
enzyme suppressants.
Desensitizing agents may be applied to exposed root surfaces to reduce sensitivity.
Receding gums surgery
Surgery is likely to be recommended if the bone surrounding the teeth has been lost.
The most straightforward surgical procedure to treat receding gums is open-flap scaling and root planing. It is similar to what was described above, except an incision is made in the soft tissue to “open” it. The infection is removed, and the gums are stitched back together.
If the bone was lost, the periodontist might place regenerative material under the gum before the final step. This is usually a tissue-stimulating protein or graft tissue (sourced from another part of your mouth).
The latter is often referred to as a soft tissue graft. The source material is often the roof of the mouth. This can be done with synthetic materials, such as gum-colored resin. This will only cover the gaps, and the body will not regenerate any tissue.
Lee explains: "Treatment varies from a 'biological reset' via deep cleaning to surgical grafts that 're-pave' the area using tissue, often from the roof of the mouth."
"To avoid the surgeon's chair, I almost always suggest switching to an electric toothbrush with a built-in pressure sensor. It effectively ends the 'scrubbing' habit and protects the delicate barrier that keeps your roots safe," he warns.
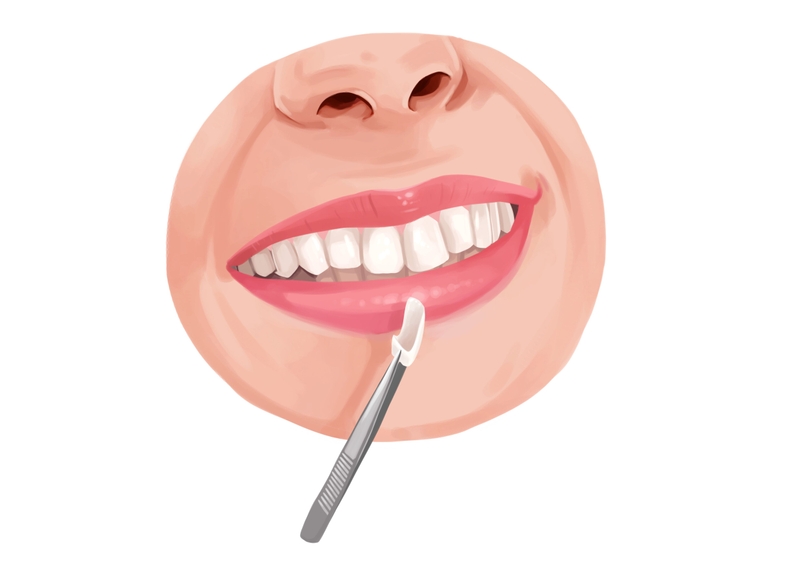
Cosmetic dentistry
Picture by Authority Dental under CC 2.0 license
Sometimes when tissue is lost, aesthetics suffer. In such a case, your dentist might recommend removable gum veneers or orthodontic intervention. Another option to cover areas with notching or sensitivity is composite bonding. Exposed root surfaces are prone to decay, and fillings may be required to address the issue.

Veneers are made from acrylic or silicone and work much like a removable denture.
Orthodontics can help move teeth to a position that makes your mouth look more uniform. This is also recommended if the positioning of your dentition makes it hard to clean or makes it easy for deep periodontal pockets to form.
How to prevent receding gums?
There are not many natural remedies for receding gums, but you can take preventive measures. These include excellent oral hygiene and changes to your diet and habits.
Brush your teeth with a soft-bristle toothbrush. Floss your teeth at least once a day. Stay up-to-date with your dental visits. If you had gum recession or periodontitis before, you may have to visit a dentist or periodontist more than twice a year.
Think about investing in antimicrobial mouthwash. You can also use a saltwater rinse.
Quit smoking and binge drinking, as such habits make your entire mouth more vulnerable to diseases and infections.
Try to incorporate foods that promote gum health into your diet, including:
nuts and seeds,
salmon and fatty fish,
cacao,
green tea,
bell peppers, and
fermented foods such as kimchi or sauerkraut.
FAQ
Can receding gums be reversed?
If caught early, gum recession can be stopped and even reversed. If there is any inflammation, however, it may be too late. Receded gum tissue does not grow back. Treatment like gum grafting is necessary to fix the issue.
Will my teeth fall out from receding gums?
Gum recession often leads to tooth loss. Pockets that form allow bacteria to enter and form a habitat. This often destroys tooth support, making the loss much more likely.
How much does it cost to fix receding gums?
If your gum recession is not severe, you may be able to get away with scaling and root planing. Costs range from $150 up to $450. In more difficult cases, when a gum graft is necessary, you will need to put aside as much as $1,200 for the surgery.
Is gum recession surgery painful?
Local anesthetics can help minimize most of the pain, but you are still likely to experience some discomfort during and after the procedure.
Harry Lee, DMD
Patients often panic when their teeth suddenly look "longer," but gum recession is usually a slow-motion process we catch during routine probing. I can often tell if a patient is right-handed just by looking at their mouth; people tend to scrub far too hard on the upper-left side, literally pushing the tissue away. This mechanical wear, coupled with the fact that nearly half of U.S. adults suffer from some form of periodontal disease, makes recession incredibly common. It is not just an aesthetic issue; once the tissue pulls back, it exposes the root's cementum, which is much softer and more sensitive than enamel.