- Root decay occurs when bacteria multiply and produce acid that breaks down the cementum layer of the tooth. Poor oral hygiene is the leading cause of tooth decay.
- Symptoms of root decay include toothache, difficulty chewing, sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, and tooth discoloration. Progressed decay causes abscesses, redness, pus, and swelling of the gums, and loose, broken, or cracked teeth.
- If caught early, it can be treated without invasive measures.
If you’re concerned about root decay, Authority Dental can help you to book a urgent dental appointment and get same-day treatment.
Learn what causes root decay (root caries), common symptoms, and treatment options. Guide to prevention and early care.
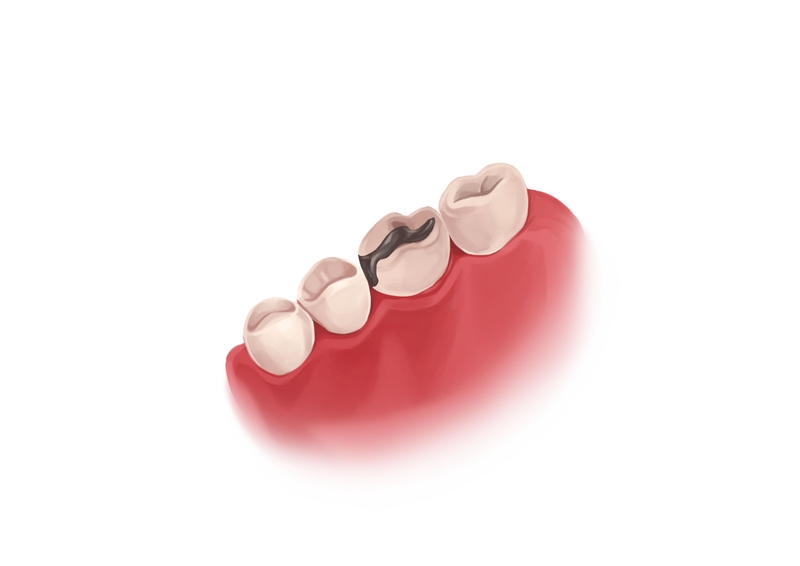
What is root decay?
Picture by Authority Dental under CC 2.0 license
Decay on the teeth happens when bacteria multiply. Their by-product is an acid that breaks down tooth structure. In root cavities, this occurs at the level of the cementum. It is much softer than enamel and much more vulnerable to these acids.
Root caries develop twice as fast as regular cavities. This is even quicker when roots are exposed, for example, due to gum recession or periodontal disease. The condition is quite common, with 9 out of 10 Americans having some untreated tooth or root decay.
Root decay symptoms
Some patients might not experience any symptoms. The diagnosis can then happen through a careful exam by a dental professional or on X-rays. Others might notice:
toothache that does not go away with medication,
difficulty in chewing,
sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures,
discoloration of the teeth,
redness, pus, and swelling on the gums, as well as
loose, broken, or cracked teeth.
If you experience any of these, report to your dentist.
What causes root cavities?
The number one cause of root decay is poor oral hygiene. Patients who do not brush and floss properly are at a high risk. Nonetheless, root caries are usually an effect of a combination of factors, including:
habits like smoking, drinking alcohol frequently, and consuming a lot of sugar,
a diet rich in acidic fruit,
aggressive brushing,
periodontal disease,
genetics,
diabetes,
stomach-related GERD,
age,
overcrowded and crooked teeth,
certain medications, and
trauma.
Aggressive brushing and gum recession tend to coincide. This is because vigorous action of soft tissues can make them sensitive and prone to infection. This, in turn, can lead to gum disease.
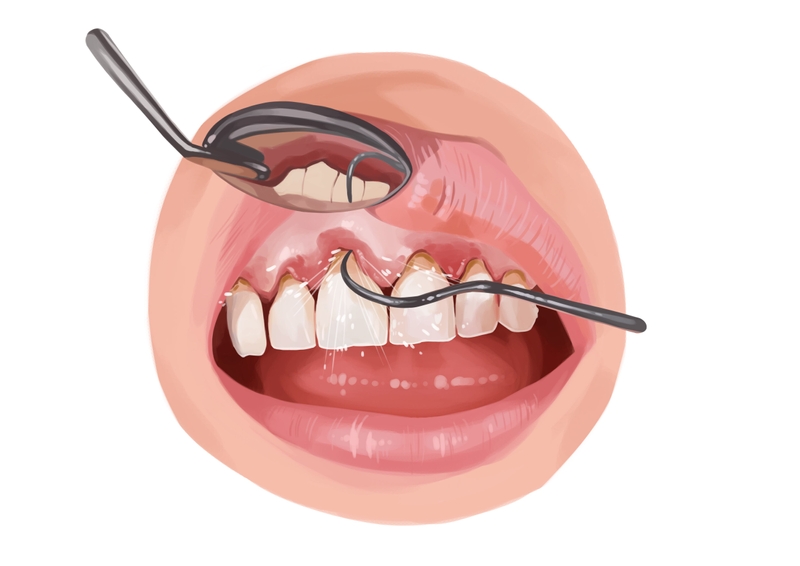
Root decay treatment
Picture by Authority Dental under CC 2.0 license
If a root cavity is caught early, the dentist may be able to reverse the process with minimally invasive treatment. This is why regular dental exams are so important. It can save you not only stress but also a lot of money.
Your dentist performs a visual exam and takes radiographs. This allows him or her to see what is happening on the surface and within the soft and hard tissues. Gum recession is usually an indicator of more severe problems; it does make root caries easier to identify.
Harry Lee, DMD warns: "The key is early detection via X-rays and regular probing. If we catch it in the 'chalky' stage, we can often stop it with prescription-strength fluoride. However, once it cavitates, it is a race against time to avoid a root canal. I always advise patients to switch to an electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor; aggressive scrubbing actually pushes the gums away, opening the door for the very decay they are trying to prevent."
Mild cases
If the decay is not severe, you may get away with less drastic measures. These include tooth remineralization and a professional teeth cleaning.
Remineralization is usually completed with fluoride treatments. You may be advised to use fluoridated prescription toothpaste and mouthwash. The dentist might also provide you with trays that you insert into your mouth every day for a short period of time. To remineralize your teeth, avoid eating, drinking, or brushing your teeth for 30 minutes after application.
A professional teeth cleaning removes plaque, calculus, and tartar that you would not be able to get rid of yourself. Special equipment is used to remove these substances from the surfaces of the teeth and between them. Such treatment is recommended at least once a year anyway.
Severe cases
There are a few ways the dentist can try to save a tooth that has a decaying root.
The first course of action is to remove the damaged area and fill the hole with restorative material. This is similar to a filling, with either composite resin or amalgam.
If the root cause was gum disease, periodontal therapy is performed. Scaling and root planing with a combination of time-release antibiotics is the way to go.
The last resort before extracting the tooth is root canal treatment. These cavities are closer to the pulp than those that appear on the surface of the enamel. If the pulp is infected, the dentist or endodontist will open the tooth to clean the canals.
Sometimes this is still not enough. A badly damaged tooth has to be extracted to prevent the rest of the mouth from becoming infected. After removing the tooth, most dentists recommend replacing the space with a fixed bridge or an implant restoration. Implant restorations prevent bone loss and other complications associated with edentulism.
The most durable solutions are dental crowns (if the tooth has survived) or implants (if the tooth was extracted).
How to prevent root caries
The following tips can help you avoid root caries and the complications that come with them.
Brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day.
Use fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash.
If you have trouble with manual dexterity, invest in an electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor.
Do not smoke or drink alcohol excessively.
Control the amount of sugar, acidic fruits, and carbohydrates in your diet.
Visit your dentist for regular dental exams and cleanings.
Ask them about in-office fluoride treatments.
Report any gum recession or mouth pain.
Alongside regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental care, some individuals include daily oral health supplements as part of their routine. Oral probiotics are designed to support balanced oral bacterial communities between dental visits. These supplements are not a replacement for professional dental treatment and should be used alongside consistent oral hygiene practices.

FAQ
What is root decay?
Root decay, also called root caries or root cavities, occurs when bacteria damage the cementum covering the tooth root, often due to gum recession or poor oral hygiene.
What are the symptoms of root decay?
Symptoms may include tooth sensitivity, toothache, discoloration near the gum line, gum swelling, abscesses, and loose or cracked teeth. Early stages may have no symptoms.
How is root decay treated?
Early root decay may be treated with fluoride therapy and improved oral hygiene. Advanced cases often require fillings, root canal treatment, or periodontal care.
Can root decay be fixed?
In most cases, yes. Your dentist will do everything he or she can to save your tooth, either through antibiotics or root canal treatment. Root caries can cause tooth loss, but only in extreme cases.
Are root cavities painful?
When caries extends to the dental pulp, you may experience acute pain. The area around your gums may also be sore.
Harry Lee, DMD
In my practice, I have often noticed that root decay is often the "silent" consequence of aging and medication. As we get older, our gums naturally recede, exposing the root's surface. Unlike the crown of your tooth, which is protected by armor-like enamel, the root is covered in cementum—a much softer tissue that dissolves twice as fast when exposed to plaque acids. I often tell patients that by the time they feel a "zing" while drinking coffee, the decay has likely already made significant headway toward the nerve because the barrier there is so thin.